Running SchemaSpy
The SchemaSpy application is able to generate useful illustrations documenting the tables present in a database, the links between them (entity relationship diagrams) and their schema structure. PGmacs includes functionality to run SchemaSpy on the database and table you are viewing, and display the relevant images in an Emacs buffer. This functionality only works in graphical mode (not in the terminal) and requires your Emacs to support SVG images; PGmacs will inform you if these conditions are not met.
SchemaSpy is free software distributed under the terms of the GNU LGPL version 3.
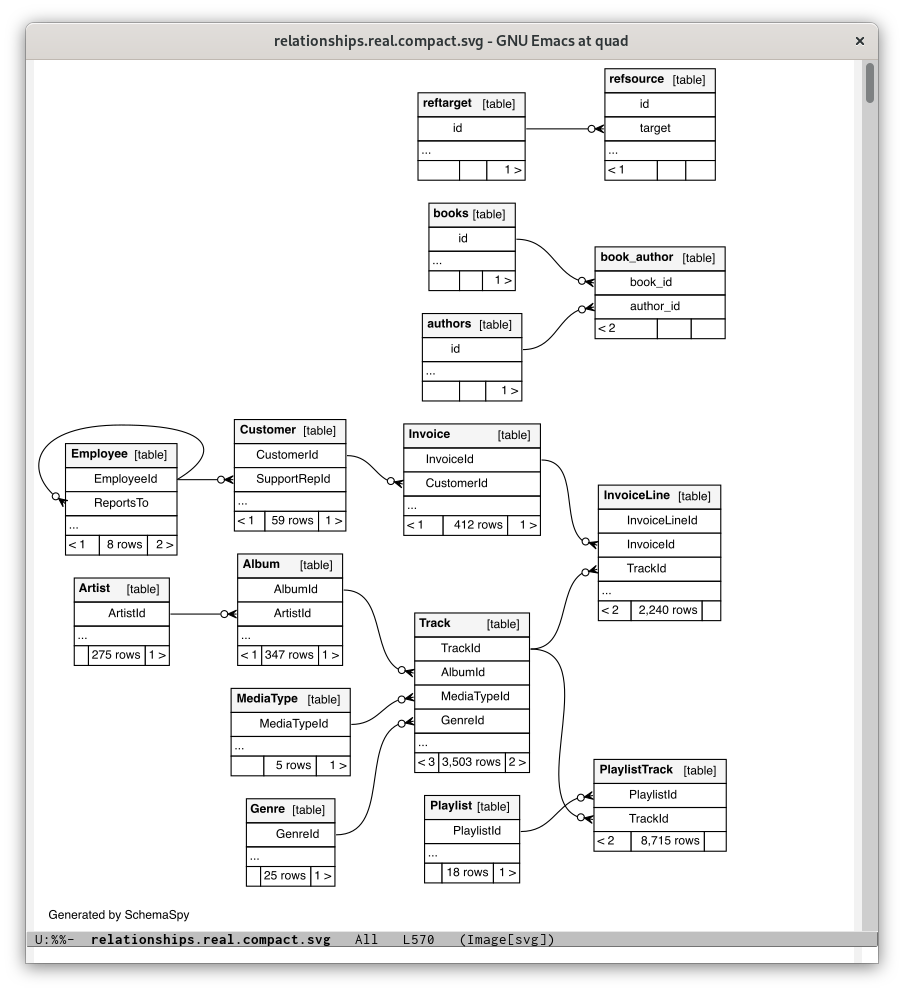
In the main table-list buffer, type S to run SchemaSpy on the current database and display the relationships between the tables in a dedicated buffer.
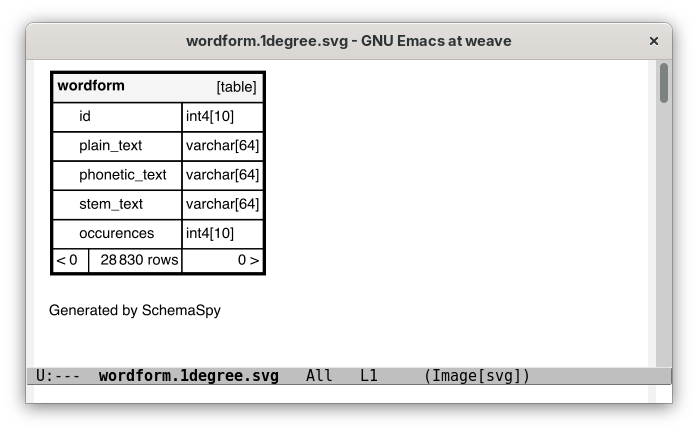
In a row-list buffer, type S to run SchemaSpy the on the current table and view the table structure diagram in a dedicated buffer.
See the customizable variable pgmacs-schemaspy-cmdline to adjust the commandline which runs
SchemaSpy to your local installation.
Running in a software container (Podman/Docker)
The default setting for pgmacs-schemaspy-cmdline runs SchemaSpy in a prebuilt Docker/Podman
software container. You will need to have Podman or Docker installed (we
recommend Podman, because it’s fully free software and it runs well in rootless mode, which is
better for security). This is the easiest way of running SchemaSpy, because all necessary
dependencies are preinstalled. The container image is around 380MB in size.
podman run -v %D:/output --network=host docker.io/schemaspy/schemaspy:latest -t pgsql11 -host %h
-port %P -u %u -p %p -db %d -imageformat svg
Some notes on customizing this commandline:
-
Replace
podmanbydockerif that is your preference. -
The official SchemaSpy container
docker.io/schemaspy/schemaspywill need network access to the host where PostgreSQL is running. (In its default configuration, SchemaSpy is not able to connect to PostgreSQL over a Unix socket.) This will require a Podman setting such as--network=host. -
In this commandline,
%dis replaced by the database name,%hby the hostname on which PostgreSQL is running,%Pby the port it is running on,%uby the user,%pby the PostgreSQL password for that user,%sby the current table schema name,%tby the current table name and%Dby the directory (which will be created in the system temporary directory) in which output files are created by SchemaSpy. The%sand%tvalues are only used in the table view, and not in the database view, and are added automatically to the commandline in the form-s %s -i %t
Running SchemaSpy installed locally
You can also run the SchemaSpy java application natively, using a setting for
pgmacs-schemaspy-cmdline similar to the following:
java -jar ~/lib/schemaspy.jar -dp /usr/share/java/postgresql-jdbc4.jar -t pgsql11 -host %h -port %P -u %u -p %p -db %d -imageformat svg -o /tmp/schema
This requires the following software to be installed:
-
SchemaSpy, in this example installed to
~/lib/schemaspy.jar -
Java (available as
javahere) -
GraphViz, installable on Debian using
sudo apt install graphvizand on Microsoft Windows usingchoco install graphvizfor example. -
JDBC support for PostgreSQL, here installed in
/usr/share/java/postgresql-jdbc4.jar, installable on Debian for example usingsudo apt install libpostgresql-jdbc-java